A geodetic datum is a reference system that defines a coordinate system, and a shape of the Earth. A geodetic datum allows positions and measurements to be identified on a curved surface, which helps maintain coordinate accuracy.
Geodetic datums
Coordinate systems used in New Zealand
Geodetic datum coordinates are normally represented by:
- latitude (Φ), which measures the distance north or south of the equator
- longitude (λ), which measures the distance east or west of Greenwich
- height (H), which measures the distance above or below the reference ellipsoid.
Geodetic datum coordinates are normally expressed as degrees (°), minutes (‘) and seconds (“) for latitude and longitude, and metres (m) for height.
For example:
- -40° 06’ 28.6294” (or 40° 06’ 28.6294” S) is a latitude south of the equator.
- 175° 16’ 54.0124” (or 175° 16’ 54.0124” E) is a longitude east of Greenwich.
- 127.899 m is a height above the reference ellipsoid.
Coordinates are usually transformed between geodetic datums by using either a transformation grid or a similarity transformation. The general approach these use is illustrated in this diagram:
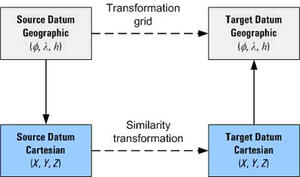
The transformation grid method uses a grid of values to map the conversion between the geodetic datums. When using this method, the coordinates remain in the geographic format (latitude, longitude, height) throughout the entire process.
Similarity transformations (also known as a 3-parameter or 7-parameter transformation) use a mathematical formula to calculate the difference between the geodetic datums. These transformations are a 3-step process because the geographic coordinates need to be changed to a cartesian (X,Y,Z) value, converted between datums, and then changed back to a geographic coordinate.
Examples for specific transformations are provided in the following sections.